

All works shown here are created using genuine mathematical algorithms written in Python.
In the mathematics of dynamical systems, an attractor is a set of values towards which a system naturally evolves over time, effectively acting like a "magnet" for the system's behaviour.
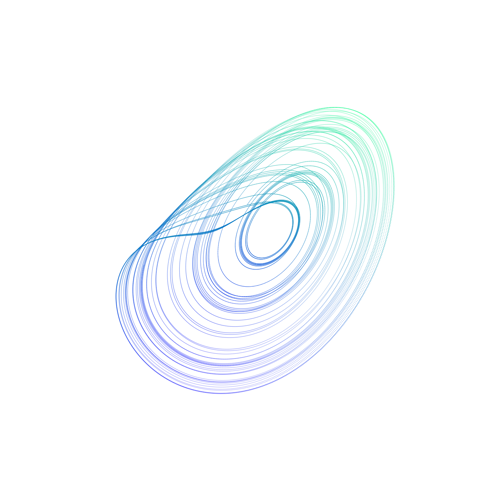 System: Chaos Theory (Continuous ODE)
System: Chaos Theory (Continuous ODE)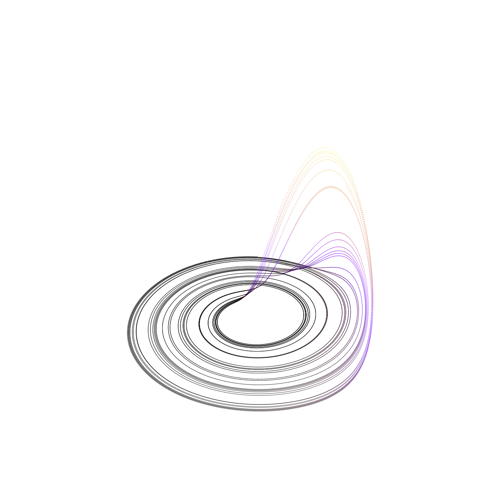 System: Chaos Theory (Continuous ODE)
System: Chaos Theory (Continuous ODE)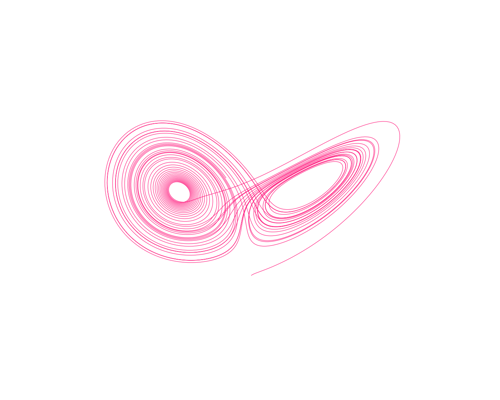 System: Chaos Theory (Continuous ODE)
System: Chaos Theory (Continuous ODE)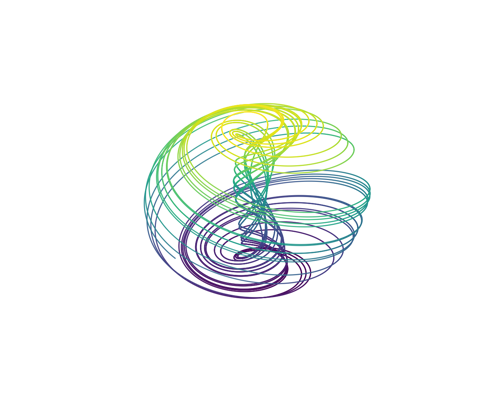 System: Chaos Theory (Continuous ODE)
System: Chaos Theory (Continuous ODE) System: Chaos Theory (Continuous ODE)
System: Chaos Theory (Continuous ODE) System: Chaos Theory (Continuous ODE)
System: Chaos Theory (Continuous ODE)Parametric curves are geometric shapes defined by equations where each coordinate is a function of a single independent variable (often "t"), allowing for the description of complex, self-intersecting paths that standard functions cannot model.
 System: 2D Parametric Curve
System: 2D Parametric Curve System: 2D Parametric Curve
System: 2D Parametric Curve System: Maurer Rose (Parametric)
System: Maurer Rose (Parametric) System: 2D Parametric Curve
System: 2D Parametric Curve System: 2D Parametric Curve
System: 2D Parametric Curve System: Damped Parametric (Harmonograph)
System: Damped Parametric (Harmonograph) System: 2D Parametric Curve (Guilloché)
System: 2D Parametric Curve (Guilloché) System: 2D Parametric Curve
System: 2D Parametric CurveFractals are infinitely complex patterns created by repeating a simple equation in a feedback loop, resulting in shapes that look the same at any scale (self-similarity).
 System: 2D Fractal (Iterated Function System)
System: 2D Fractal (Iterated Function System) System: 2D Fractal (Chaos Game)
System: 2D Fractal (Chaos Game) System: 2D Fractal (Iterated Function System / L-System)
System: 2D Fractal (Iterated Function System / L-System) System: 2D Fractal (Inverse Iteration Method)
System: 2D Fractal (Inverse Iteration Method)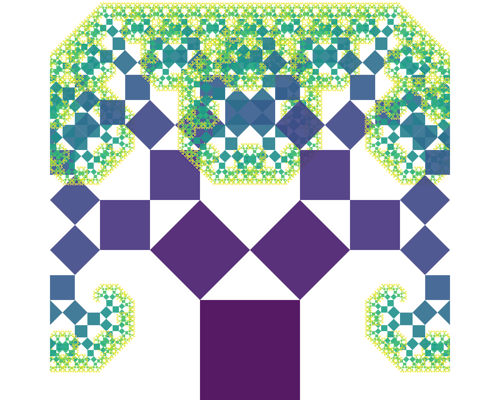 System: 2D Fractal (Geometric Recursion)
System: 2D Fractal (Geometric Recursion)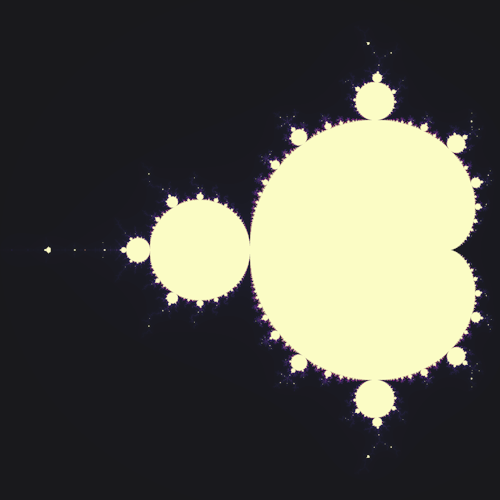 System: 2D Fractal (Complex Dynamics)
System: 2D Fractal (Complex Dynamics) System: 2D Fractal (Iterated Function System)
System: 2D Fractal (Iterated Function System) System: 2D Fractal (Complex Dynamics)
System: 2D Fractal (Complex Dynamics)Tessellations are patterns formed by repeating geometric shapes to cover a surface completely without any gaps or overlaps.
 System: 3D Tessellation
System: 3D Tessellation System: 2D Tessellation
System: 2D Tessellation System: 3D Tessellation
System: 3D Tessellation System: 2D Tessellation
System: 2D Tessellation System: 3D Tessellation (Space Filling)
System: 3D Tessellation (Space Filling) System: 2D Tessellation (Aperiodic)
System: 2D Tessellation (Aperiodic)A minimal surface is a shape that naturally finds the most efficient way to stretch across a boundary, using the least amount of surface area possible.
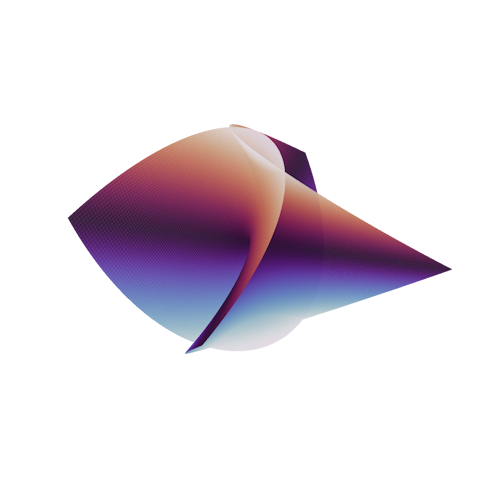 System: Minimal Surface (Differential Geometry)
System: Minimal Surface (Differential Geometry)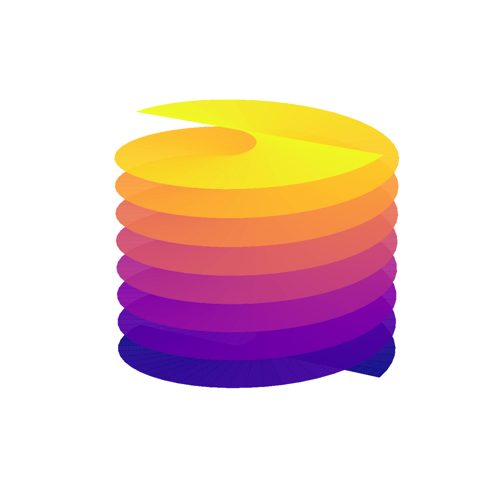 System: Minimal Surface (Ruled Surface)
System: Minimal Surface (Ruled Surface)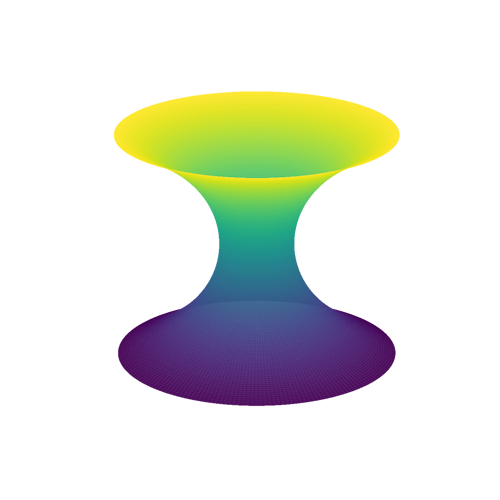 System: Minimal Surface (Surface of Revolution)
System: Minimal Surface (Surface of Revolution)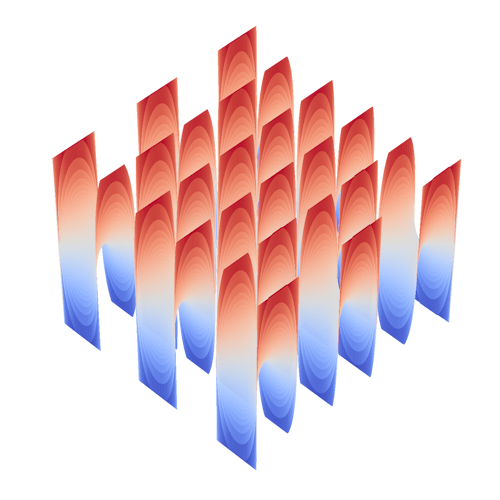 System: Minimal Surface (Doubly Periodic)
System: Minimal Surface (Doubly Periodic)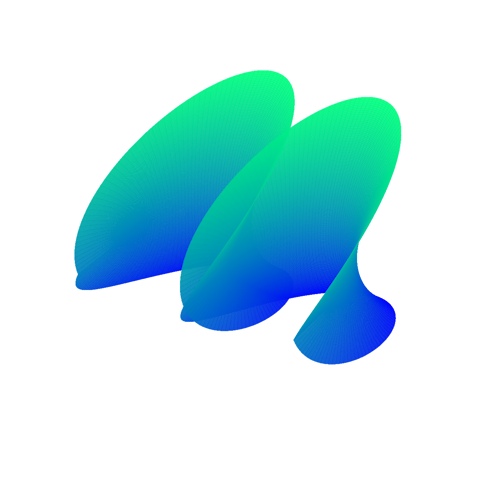 System: Minimal Surface
System: Minimal Surface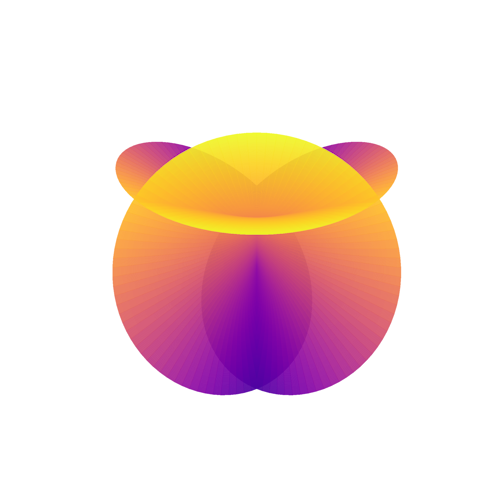 System: Minimal Surface (Non-orientable)
System: Minimal Surface (Non-orientable)